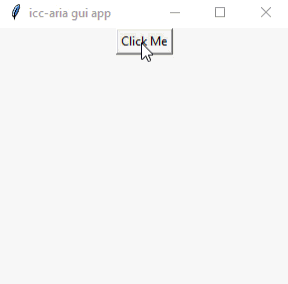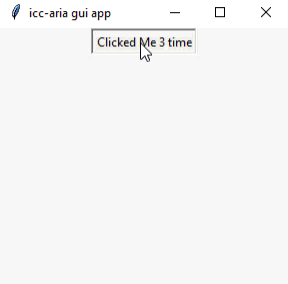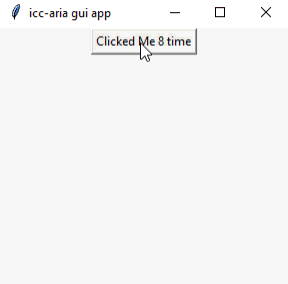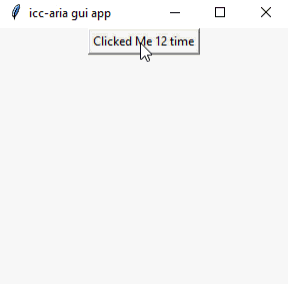
در این قسمت سعی می کنیم تا یک عملیات بسیار ساده را طرح ریزی کنیم و برای کلید مورد استفاده قرار دهیم. که ابن عملیات شامل نمایش یک خروجی و اجرای یک تابع پس از اجرای کلید خواهد بود. نمونه کد:
# Function Example
#importing modules
from tkinter import *
#making a function for button clicked
def btn_pushed():
print("clicked")
#making a window instance
window = Tk()
#creating a title for window
window.title("icc-aria gui app")
#making a label inside the window
Label(window,text="Push the button to see the action").pack()
#making the button to do an action
Button(window,text="Click Me!",command=btn_pushed).pack()
#making a loop for the window to run
window.mainloop()
# OOP Example
# importing tkinter modules
from tkinter import Tk,Button,Label
# inherianceing from Tk module and initializing the Tk class for creating object
class App(Tk):
def __init__(self):
Tk.__init__(self)
self.title("icc-aria gui app")
#making a label inside the window
Label(self,text="Push the button to see the action").pack()
#making the button to do an action
Button(self,text="Click Me!",command=self.btn_pushed).pack()
#making a function for button clicked
def btn_pushed(self):
print("clicked")
# creating the object of app for tk main window
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = App()
app.mainloop()
نمونه خروجی:
اما بهتره کمی کار رو مفهومی تر کنیم و به ازای هر بار کلیک بر روی کلید یک شمارنده را بر روی آن قرار دهیم که با هر بار کلیک یک مقدار به واحد اولیه آن اضافه و بر روی کلید مورد نظر نشان دهد. در واقع این کار با استفاده از یک تابع که به صورت مجزا بر روی تنظیمات کلید ساخته شده است عمل می کند و با هر بار کلیک عملیات مورد نظر را انجام می دهد.
# Function Example
#importing modules
from tkinter import *
#a variable to hold the counted times button pushed
counter = 0
#making a function for button clicked
def btn_pushed():
#making changes to global variable of counter
global counter
counter +=1
#changing the configuration of btn with every click
btn.configure(text="Clicked Me {} time".format(counter))
#making a window instance
window = Tk()
#creating a title for window
window.title("icc-aria gui app")
#making a button inside the window
btn = Button(window)
#configuring the button
btn.configure(text="Click Me",command=btn_pushed)
#packing the button to insert in window
btn.pack()
#making a loop for the window to run
window.mainloop()
# OOP Example
# importing tkinter modules
from tkinter import Tk,Button,Label
# inherianceing from Tk module and initializing the Tk class for creating object
class App(Tk):
def __init__(self):
Tk.__init__(self)
self.title("icc-aria gui app")
self.counter = 0
#making a button inside the window
self.btn = Button(self)
#configuring the button
self.btn.configure(text="Click Me",command=self.btn_pushed)
#packing the button to insert in window
self.btn.pack()
#making a function for button clicked
def btn_pushed(self):
self.counter +=1
self.btn.configure(text="Clicked Me {} time".format(self.counter))
# creating the object of app for tk main window
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = App()
app.mainloop()
نکته: اگر دقت کنید در قسمت معرفی command ما تابع را بدون پرانتز قرار دادیم چون به صورت یک صفت بر روی کلید عمل خواهد کرد.
نمونه خروجی: